Applying the Standards
Read about which standards to use when carrying out identification processes.
Table 1 describes broad identification scenarios and the applicable assurance standards.
| What are you trying to do? | Applicable standard |
|---|---|
|
Enrolment Gathering information and linking it to an entity enrolling for the first time |
Information Assurance Standard Binding Assurance Standard |
|
Recognition setup Adding an authenticator so an entity can be recognised when they return
|
Binding Assurance Standard Authentication Assurance Standard |
|
Ongoing recognition Ensuring the same entity is returning to access the system |
Authentication Assurance Standard |
|
Maintenance Collecting more information from the entity or updating/removing the information already held |
Information Assurance Standard Binding Assurance Standard |
|
Credentials Establishing credentials for use across multiple contexts |
Information Assurance Standard Binding Assurance Standard Authentication Assurance Standard Federation Assurance Standard |
Expanding on the Enrolment process
The identification management element Enrolment, that connects an Entity to a Relying party (see About identification management), expands the three-way relationship between the Entity, their Information and any Authenticator in the context of a Relying Party.
About identification management
Diagram 1: Relationship between the enrolment identification management elements
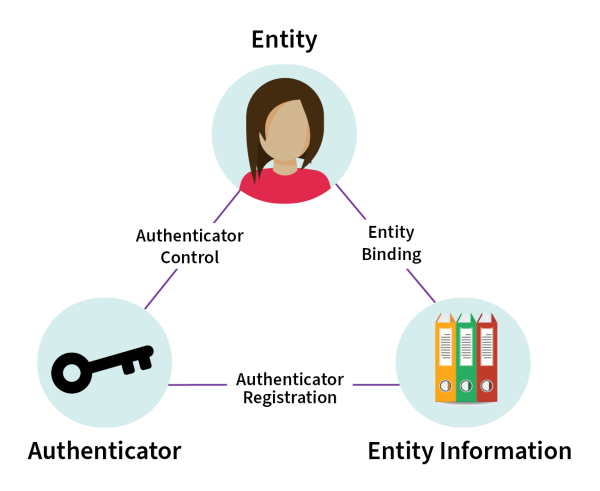
Detailed description of diagram
This diagram shows a triangle representing the connection between the 3 elements: Entity (represented by a person) at the top of the triangle, Authenticator (represented by a key) at the bottom left, and Entity Information (represented by folders of information) at the bottom right.
The connection between Entity and Entity Information is labelled Entity Binding. The connection between Entity Information and Authenticator is labelled Authenticator Registration. The connection between Authenticator and Entity is Authenticator Control.
Level of assurance
Level of assurance (LoA) is the indicator of the robustness of the identification processes taken to establish an entity’s information in a system.
LoA cannot be expressed as a single value or an accumulated value due to the independence of each identification process. Therefore, it is represented by an expression of the levels achieved by each identification process.
For example, the level of assurance of enrolled information relating to an entity, where an authenticator has been issued would be expressed as:
LoA = {IAn, BAn, AAn}
Where n represents the assurance level achieved by each identification process.
LoA is useful as an indicator of assurance profiles, such as those:
- required to meet a certain risk profile — as the result of having carried out an assessment of identification risk
- resulting from an assessment of the current capability of an identification management process
- needed for trust in an identification process.
If an organisation is providing Credentials then a separate indication of ‘FA’ compliance is also desirable.
Compliance with the standards
Compliance terminology
All the identification standards use the keywords MUST, SHOULD, MAY and their negatives, to signify different types of requirements as defined by RFC 2119:
MUST — signifies an absolute requirement.
SHOULD — defines a recommended course of action that may be ignored if the full implications of doing so are clearly understood and the organisation is prepared to accept them.
MAY — defines a course of action that is truly optional.
Mandated compliance
Mandated compliance with these standards will be provided through such mechanisms as contracts, cabinet mandates and legislation.
When mandated, an organisation will be prepared, when notified, to assess and report on its compliance with these standards. The assessment methodology and reporting mechanism will be communicated to organisations at the time of notification.
Self-assessed compliance
Any individual or organisation can choose to use these standards as a guide to good practice.
The risk of non-compliance
If an organisation does not fully meet the standards, they accept any risks associated with not doing so. For example, the increased possibility that a customer’s information will be breached.
Non-compliance can also impact the ability for an organisation to participate in federated or other trusted arrangements.
Exemptions
Currently no process exists by which a mandated organisation can secure an exemption from the requirement to meet these Standards.
Utility links and page information
Last updated

